Nominal G-force of Vibration
Instantaneous G-force vs Phase-IV G-force
Measuring the acceleration of a vibration plate may appear straightforward, but the definition of G-force you apply can dramatically change the reported value. Instantaneous peak G-force, often claimed by manufacturers, does not represent the real vibration loading experienced by the user.
This article explains the concept of Nominal G-force, based on Phase-IV interval acceleration, and compares it with the commonly quoted instantaneous G-force.
What Is Instantaneous G-force?
The G-force of vibration fluctates between a positive maximum and a negative maximum with alternating direction. Instantaneous G-force refers to the acceleration of at a certain moment in the vibration cycle.
Using the Simple Harmonic Model, the instantaneous acceleration is expressed as:
The instantaneous peak acceleration occurs at the crest of the sine wave:
Converted to maximum G-force:
Instantaneous G-force only represents the acceleration at a specific moment in the vibration cycle. It does not reflect how acceleration behaves over time or indicate whether that acceleration contributes to meaningful loading on the user’s body.
Because instantaneous G-force is a fluctuating value, manufacturers tend to quote the maximum G-force for their vibration plates, which leads to inflated and misleading claims.
The Nature of Vibration Acceleration
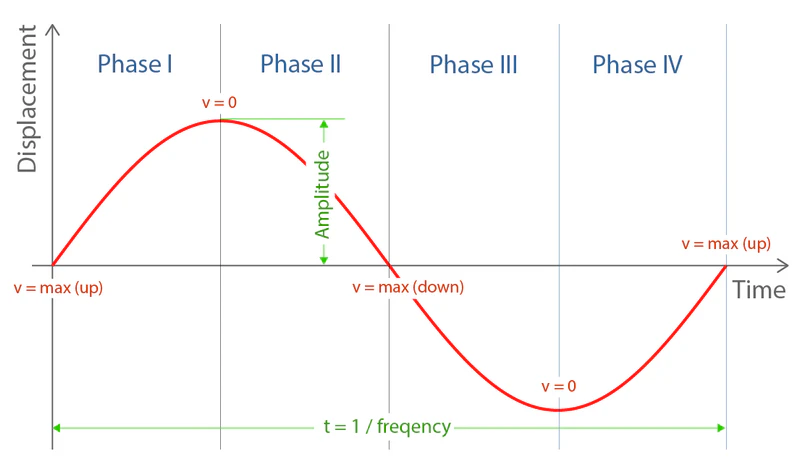
Vibration motion is different from one-directional movement. Its velocity and acceleration change continuously, reverse direction periodically, and form a repeating four-phase pattern. The loading effect on the user varies from phase to phase. Only one of these phases, Phase IV, produces upward acceleration that adds to the user’s body weight.
Instantaneous G-force does not distinguish between phases or directions and therefore does not represent the real loading associated with vibration plate exercise.
Phase-IV Interval Acceleration
Phase-IV acceleration is obtained by applying the basic acceleration definition:
In Phase IV, velocity increases from 0 to vmax, and the time interval of this phase is 1/(4f). This gives:
Converted to G-force:
Phase IV is the only phase that produces positive upward acceleration that adds to gravity, creating additional downward load on the user’s body and stimulating muscle activation. This interval acceleration forms the basis of the Nominal G-force of a vibration plate.
What Is Nominal G-force?
Nominal G-force is a practical and representative measure of vibration intensity based on the Phase-IV interval acceleration. It is derived from the portion of the vibration cycle that contributes to actual mechanical loading on the user.
Nominal G-force is defined as:
The purpose of Nominal G-force is to provide a simple, realistic, and comparable metric for evaluating vibration plates, avoiding the exaggeration associated with peak instantaneous values. Unlike instantaneous G-force, which fluctuates continuously and usually does not correspond to meaningful loading, Nominal G-force reflects the actual upward acceleration that adds to the user’s body weight.
Because Nominal G-force is based on the physics of the vibration cycle rather than marketing claims, it offers a fair and consistent way to compare vibration plates using the same frequency and amplitude basis.
Comparison: Instantaneous vs Phase-IV (Nominal) G-force
| Instantaneous G-force | Phase-IV (Nominal) G-force |
Why Nominal G-force Is the Better Metric
- Represents real mechanical loading on the user’s body
- Derived from interval acceleration across the Phase-IV segment
- Avoids inflated values from instantaneous peaks
- Provides a consistent standard for comparing vibration plates
- Aligns with the physics of vibration motion, not marketing claims
Summary
- Instantaneous G-force only describes the peak acceleration at a single point in time.
- Vibration acceleration fluctuates and must be understood in terms of phases.
- Only Phase IV produces upward acceleration that adds to gravity.
- Phase-IV interval acceleration provides a meaningful measure of loading.
- Nominal G-force, based on Phase-IV acceleration, is the most realistic metric for vibration plate intensity.
This Nominal G-force model offers a scientifically consistent and practical way to evaluate vibration plates and compare their performance using the same reference standards.